Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden flow of electricity between two objects with opposite electrical charges. It happens when an object carrying a positive charge comes into contact (or close proximity) with one carrying a negative charge. The result is a brief electrical current, sometimes even visible as a spark.
Most of us have experienced a mild form of ESD firsthand, like feeling a small shock after walking across a carpeted floor and touching a metal doorknob. While harmless in everyday life, these same static discharges can be highly destructive in industrial environments, where sensitive electronic components or volatile materials are involved.
Why Electrostatic Discharge Matters
In manufacturing systems and process control environments, ESD can cause:
- Component Failure: Solid-state devices and integrated circuits are particularly sensitive to voltage spikes caused by ESD
- Safety Hazards: In hazardous or explosive atmospheres, a discharge event can ignite flammable gases or dust
- Operational Downtime: Damaged sensors, transmitters, or controllers can disrupt entire production systems
Because ESD can originate from simple, commonplace causes, such as contact between charged materials, electrical shorts, or dielectric breakdown, preventive measures are critical for both safety and reliability.
How Manufactures Prevent ESD

To mitigate the risk of ESD damage, leading manufacturers integrate multiple layers of protection into product design and handling. These include:
- Material Selection: Avoiding materials that hold static charge and using non-conductive or static-dissipative materials in sensitive assemblies
- Grounding Practices: Providing detailed grounding instructions for technicians and end users to ensure static charges are safely neutralized
- Workplace Controls: Maintaining proper humidity levels, using anti-static wrist straps, mats, and grounding cords in assembly or test areas
By addressing ESD at both the product and operational levels, manufacturers ensure instruments maintain long-term reliability, even in the most challenging industrial environments.
The Role of Proper Grounding
Grounding is the most effective safeguard against ESD. When components and enclosures are properly grounded, excess static charge dissipates safely into the earth. In contrast, ungrounded or poorly grounded systems can accumulate charge until it discharges unpredictably, potentially through a sensitive electronic path.
Investing in quality components and ensuring proper grounding not only extends product life but also enhances operator safety and process stability.
When Certain Products Are More Susceptible
Some instruments are naturally more prone to ESD exposure due to their operating environments. For example, duct-mounted humidity transmitters are frequently installed in moving airstreams, where friction between air and probe surfaces builds up static charge.
Charged ions traveling down the probe often follow the path of least resistance—through the protective cap or filter that shields the humidity sensor. This is why the material composition and spacing of that protective layer are so important. A well-designed filter made from static-dissipative materials can significantly reduce ESD risk while maintaining accurate humidity measurements.
Innovative Solutions from

Series RHP – Humidity & Temperature Transmitter
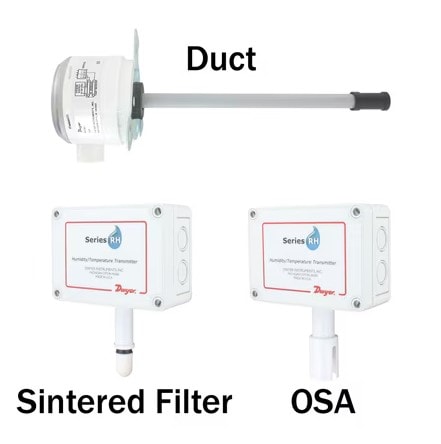

The Series RHP Humidity and Temperature Transmitter delivers precise, stable, and reliable measurements even in environments prone to electrostatic discharge. Engineered with advanced polymer capacitance sensing technology and robust mechanical construction, the RHP offers long-term accuracy across HVAC, air quality, and industrial monitoring applications. Its durable housing, optional display, and configurable outputs make it ideal for both system integration and retrofit projects where ESD protection, measurement integrity, and operational efficiency are critical.
Key Features:
- Dual Output Efficiency: Combines voltage or current humidity outputs with passive temperature thermistor or RTD signals, reducing installation costs
- Flexible Performance: Offers 2 %, 3 %, or 5 % accuracy options for a wide range of applications
- Environmental Protection: A radiation shield guards against radiant heat, lowering overall system operating costs
- Display Options: Duct-mount versions are available with a two-line alphanumeric LCD for real-time visibility
- Traceable Accuracy: Optional NIST calibration ensures compliance with industry standards and quality requirements
Applications: The Series RHP is well-suited for a variety of environmental and HVAC control applications. It provides reliable monitoring for air economizers, serves as a dependable outdoor temperature and humidity reference, and maintains precise conditions in pool rooms and other high-humidity spaces. Its versatility also makes it an excellent choice for general HVAC environmental control, where consistent measurement and ESD resistance are essential for system performance and energy efficiency.
Connect with a DwyerOmega Expert Today!