 Hospital Room Air Quality Monitor
Hospital Room Air Quality Monitor Question: If you’ve ever spent time in a hospital, you may have noticed a device similar to a home thermostat mounted on the wall with a display stating “ACH”. What exactly does “ACH” stand for and why is it important in a building or hospital?
Answer: ACH stands for Air Changes per Hour. It refers to the number of times the air within a room is completely replaced with fresh air within one hour. In hospitals and other critical environments, maintaining a proper ACH rate is essential for infection control, air quality, and overall health safety. Higher ACH values help remove contaminants, control humidity, and ensure proper ventilation.
What is ACH?
Air changes per hour (abbreviated as ACPH or ACH) or air change rate is a measure of the air volume added to or removed from a space divided by the volume of the space. Simply put, air changes per hour are the number of times you change over the total volume of air in a defined room or space. Air changes per hour are calculated by first determining the volume of the space you will be exchanging air in. This is calculated by multiplying the length by width by height of the room.
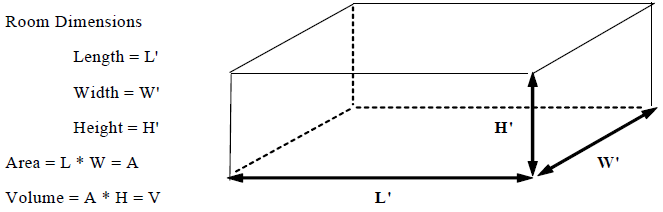
To calculate the air changes per hour, multiply the incoming or supply air flow rate (Q) in units of cubic feet per minute (CFM) by 60 minutes per hour, and then divide that number by the volume of the room. One "air change" results when all of the air in the room has been replaced.
ACH = (60 × Q) ÷ Vol
Q = Supply air flow in CFM
Vol = Space volume calculated by L × H × W in cubic feet
Why is ACH important?
Homes and workplaces are full of potential contaminants ranging from VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) to common dust. Proper ventilation and the exchange of air is the best way to reduce the presence of these pollutants, maintaining a healthy living and working condition.
Dating all the way back to 1973, ASHRAE has provided a set of standards for minimum ventilation requirements in commercial and residential applications that is found in ANSI / ASHRAE 62.1 and 62.2. These standards are incorporated into the design and size requirements of air handling equipment to ensure the space classification is seeing an adequate amount of air changes.
 Air Changes per Hour in Office and Hospital Spaces
Air Changes per Hour in Office and Hospital Spaces Question: What are typical air changes per hour (ACH) values in commercial and hospital environments, and how are they monitored?
Answer: In commercial office spaces, air changes per hour typically range from 6 to 8. In contrast, hospital operating rooms and patient rooms may have ACH values of up to 25. Thermostat-style devices in these spaces continuously display air change rates, allowing medical staff to ensure safe working conditions.
To monitor ACH, individuals can measure the supply air entering a room and the exhaust or return air. This can be done using test and balance instrumentation, such as air flow hoods to measure diffuser air flow, or anemometers and Pitot tubes to monitor air flow in supply or return ducts.
 Air Velocity Transmitter, Series AVUL
Air Velocity Transmitter, Series AVUL Question: What are the options for permanently monitoring air velocity in a building management system?
Answer: For permanent installations, devices such as averaging Pitot tubes, air flow stations, or hot wire anemometer transmitters can be used to provide real-time air velocity measurements to a building management system. These instruments help simplify the calculation of air changes per hour and ensure a comfortable environment for occupants.
DwyerOmega offers a range of air flow monitoring instruments to support air quality management. To learn more about these products, please contact us at 219-879-8000 or tech@DwyerOmegamail.com.

